Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Accounting for the formation of financial results, the value, importance and characteristics of accounts. Classification of income and expenses of the organization. Financial result for the purposes of accounting and tax accounting. Accounting for financial results on the example of Fortuna LLC.
term paper, added 11/30/2010
Report models in international practice. The role of auditing standards in the regulation of auditing activities in the Russian Federation. Audit of accounting organization and accounting policy. Audit of income and expenses for ordinary activities.
term paper, added 09/18/2007
The concept and structure of the formation of the financial result. Analysis of the composition and dynamics of the firm's balance sheet profit. Accounting for operating and non-operating income and expenses. Reflection in the financial statements of the financial results of the enterprise.
thesis, added 04/16/2010
The concept and structure of the financial result, income and expenses of the organization in accounting. Features of accounting for profits and losses of the organization. The procedure for the formation of the financial result, its accounting on the example of OOO TP "Elektromash-Kratu".
term paper, added 12/08/2013
Methods of accrual and accounting of depreciation of fixed assets at the enterprise. Accounting for the cost of producing finished products and the financial result from its sale. Calculation of the cost price and distribution of costs by types of products.
term paper, added 05/24/2014
Accounting for income, expenses and financial results for the current activities of a budgetary institution. Conclusion of accounts of the current financial year on the current activities of a budgetary organization. Accounting for the financial result of the cash execution of the budget.
test, added 02/27/2009
The concept of income and expenses of the organization and their classification in the income statement. The methodology for calculating the financial result in the form of reporting and the procedure for the formation of indicators. Legal framework and reporting tasks.
term paper, added 05/24/2015
Essence, tasks and types of analysis of the economic activity of a construction company
Financial results and evaluation of the efficiency of economic activity of construction enterprises
Economic analysis as a science is a system of special knowledge based on the laws of development and functioning of systems and aimed at understanding the methodology for assessing, diagnosing and forecasting the financial and economic activities of an enterprise.
The subject of economic analysis is economic processes, their socio-economic efficiency and the final financial results of activities, which are formed under the influence of external and internal environmental factors and are reflected through the system of economic information.
Rice. 1. Types of analysis of the economic activity of a construction company
Tasks of economic analysis:
1) increasing the scientific and economic feasibility of business plans, standards;
2) an objective and comprehensive study of the implementation of business plans and compliance with regulations;
3) determination of the effectiveness of the use of labor, material and financial resources;
4) control over the implementation of the requirements of commercial accounting;
5) identification of internal reserves;
6) checking the optimality of management decisions.
The basis of the economic development of a construction organization is profit, which acts as an indicator of the effectiveness of the organization, the source of its life. The growth of profits creates a financial basis for providing production activities with their own financial resources, for the implementation of expanded reproduction and for meeting the social and material needs of the workforce. At the expense of profit, the organization's obligations to the budget, banks and other organizations and institutions are fulfilled. However, since the profit of an enterprise is the most important source of formation of the federal budget and the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, in this regard, the mechanism for the formation of the financial results of the enterprise should be considered from the position of tax accounting. This is due to the fact that the net profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise is the difference between the amount of the balance sheet (gross) profit and the amount of income tax directed to these budgets.
Consequently, not only economic entities themselves, but also the state are interested in increasing the amount of profit.
The calculation base is book profit- the main financial indicator of the production and economic activities of enterprises. For tax purposes, a special indicator is calculated - gross profit, and on its basis taxable income. The part of the balance sheet profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise after making taxes and other payments to the budget is called net profit, which characterizes the final result of the enterprise.
balance sheet profit(P b) is formed from the financial result from the sale of products (works, services), goods and other tangible assets (fixed assets, intangible assets, tangible working capital and other assets), defined as the difference between the proceeds from sales and the amount of expenses or the cost of sales of products (works, services) and other tangible assets, as well as income from non-sales operations, reduced by the amount of expenses on these operations:
P b \u003d P sd + P and + P vsp + V d - R (1)
where P sd - profit from the delivery of work and services;
P and - profit from the sale of property;
P vsp - profit from the sale of products of auxiliary and auxiliary industries;
In d - non-operating income (losses);
P - expenses for the implementation of non-sales operations.
The main component of the balance sheet profit of the enterprise is from the sale of manufactured products (works, services), the share of which in the amount of gross profit is 90 - 95%.
Profit from delivery of works to the customer (P sd) is determined:
P sd \u003d O smr - SS pl (2)
where About CMR - the estimated cost of construction and installation works;
SS pl - the cost of construction and installation works.
Profit from the delivery of work performed to the customer, depending on the stage of the investment process, can be estimated, planned and actual.
The estimated profit is understood as the profit determined in the process of developing design and estimate documentation.
Planned profit (P pl) is a profit forecast for a construction organization. It consists of the estimated profit (SP) and the planned cost savings from reducing the cost of construction and installation works (E ss), planned based on the effect of the developed organizational and technical measures and compensation received from the customer (K).
P pl \u003d SP + E ss + K (3)
The actual profit (P f) from the delivery of work performed to the customer is determined as the difference between the proceeds from their sale (contractual price - D c) without value added tax VAT and the costs of their production and sale (actual cost of construction and installation works - CC f) .
P f \u003d D c - VAT - SS f (4)
Profit from the sale of fixed assets and other property represents a financial result that is not related to the main activities of the enterprise. It reflects the profit from other sales, which includes the sale to the side of various types of property listed on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
Financial results from non-operating operations- this is profit (loss) on operations of a different nature, not related to the main activity of the enterprise and not related to the sale of products, fixed assets, the performance of work and the provision of services. The composition of non-operating profits (losses) includes monetary amounts of received and paid fines, penalties, forfeits and other economic sanctions; interest received on the amounts of funds on the organization's accounts, exchange rate differences on foreign currency accounts and operations in foreign currency; income (dividends, interest) on shares, bonds and other securities owned by the organization, as well as income from equity participation in the activities of other organizations and enterprises; other income, expenses and losses.
The amount of profit of the enterprise subject to taxation(tax base for income tax) is determined in accordance with Ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The tax rate is set at 20%. Wherein:
· the amount of tax calculated at the tax rate of 7.5% is credited to the federal budget;
· the amount of tax calculated at a tax rate of 14.5% is credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
· the amount of tax, calculated at a tax rate of 2%, is credited to local budgets.
The amount of profit received after paying income tax is called net profit. From net profit, the enterprise makes payments on borrowed capital (repayment of loans), makes payments for excess emissions of pollutants into the environment. The difference between net profit and these payments represents net profit, remaining at the disposal of the enterprise.
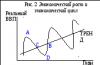
The company uses the amount of net profit received independently. The distribution of net profit is one of the areas of intra-company planning. The distribution of this profit is made, as a rule, for the formation of an accumulation fund, a consumption fund and a reserve (insurance) fund. The order of formation and use of profit is presented in fig. 2.
Rice. 2. The procedure for the formation and use of enterprise profits
accumulation fund, which also includes the amount of depreciation, is mainly used for the technical and social development of the enterprise. At the expense of this, it acquires new tangible assets, including the creation of new fixed assets for both production and non-production purposes. In addition, the funds of the fund can be used for scientific research and for the implementation of environmental protection measures.
reserve fund created to cover unforeseen expenses caused by natural disasters. The size of this fund must comply with the constituent documents.
consumption fund used to finance material incentives for employees of the enterprise and for social needs. Thus, in particular, from this fund can be paid: bonuses not related to performance indicators (for long-term work, in connection with anniversaries, etc.); material aid; sanatorium and resort vouchers, medicines and treatment of employees of the enterprise; dividends to shareholders of the enterprise.
In this work, the procedure for the formation and accounting of the financial results of the organization Kalina LLC was studied. This organization is engaged in construction.
Accounting in the organization in question is maintained in accordance with the regulatory and legislative acts of the Russian Federation. The legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting as a whole consists of the Federal Law "On Accounting", which establishes a unified legal and methodological basis for organizing and maintaining accounting in the Russian Federation, other federal laws, decrees of the President of the Russian Federation, resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation, Regulations on accounting accounting approved by the Ministry of Finance.
Since this organization is engaged in construction, accounting is carried out taking into account the specifics of the activity. The participants in a construction contract are contracting construction organizations, construction ordering organizations and investors. The specifics of business transactions, as well as the specifics of the process of cash flow, determine the specifics of the formation of financial results for each of the participants in this agreement. At different stages of its development, Kalina LLC acted both as a construction contractor and as a construction customer.
The final financial result (balance sheet profit or loss) of the activities of a construction contractor is made up of the financial result from the delivery of objects, works and services provided for by the contracts to the customer, the sale to the side of fixed assets and other property of the construction organization, products and services of auxiliary and auxiliary industries located on balance sheet of the construction organization, as well as income from non-sales operations, reduced by the amount of expenses on these operations (other income, reduced by the amount of other expenses).
In accordance with PBU 2/2008, the financial result of the developer for activities related to construction is determined as the difference between the amount (limit) of funds for its maintenance, included in the estimates for facilities under construction in this reporting period, and the actual costs of its maintenance
A significant part of the work is devoted to the analysis of financial performance. At first glance, the organization cannot be given a positive assessment of solvency, market stability, profitability and financial stability. Most of the calculated indicators either have values below the norm, or show a negative trend for 2012-2014. However, when analyzing financial indicators, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of the organization's activities and only after that make a final conclusion.
Kalina LLC is currently engaged in the construction of a large facility (a residential complex consisting of several houses) and acts as a developer, not a contractor, and the construction has not yet been completed, therefore, the financial result has not yet been received. This analysis will be more correct to do after the completion of construction and sale of apartments. In 2014, there is practically no revenue, there is a very small amount of money on the company's accounts, the organization's accounts have a large amount of debt, both long-term and short-term, therefore, the calculated solvency indicators are below the nominal value.
Most indicators of the market stability of Kalina LLC are below the norm, the reason for this is the unfinished process of building a large residential complex. At the end of 2014, the organization has a large amount of other non-current assets and a relatively small amount of retained earnings, as a result of which the organization's non-current assets exceed capital and reserves by more than four times.
When analyzing the dynamics of profitability indicators for 2014, either a sharp increase in values or their reduction is observed. The reason for this is a sharp reduction in revenue and cost of sales, and as a result, a reduction in sales profit and net profit.
The solution to existing problems in the organization can be the completion of the first stage of construction and the beginning of the sale of apartments. The organization will begin to receive revenue, the amount of money on its bank accounts will begin to grow and liabilities will decrease, both to banks and to investors. And as a consequence, against the background of these positive changes, most of the calculated solvency indicators should have values within the normal range.
The analysis of absolute indicators of financial stability and the construction of a three-component indicator clearly showed that the Kalina LLC company had impaired financial stability and solvency at the time of the analysis, but the organization has all the prerequisites for restoring financial well-being. As mentioned above, in order to achieve this goal, the company should complete the construction of a large residential complex, start selling apartments, and as a result, receive cash, revenue, profit, reduce the size of non-current assets and accounts payable.
List of used sources.
1. Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Part One) of December 18, 2006 No. 230-FZ.
2. Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
3. Federal Law "On Accounting" dated November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ.
4. Regulations on the composition of costs for the production and sale of products (works, services) included in the cost of products (works, services), and on the procedure for the formation of financial results taken into account when taxing profits. Approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 05.08.92 No. 552.
5. Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On Approval of the Chart of Accounts for Accounting of the Financial and Economic Activities of Organizations and Instructions for Its Application” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n.
Organization finances. Cribs Zaritsky Alexander Evgenievich
97. Financial result of the construction organization
The construction organization makes independent planning of the cost of work. This planning is a component of the development of financial plans on the basis of concluded contracts.
Elements included in the cost of construction works:
1) costs directly related to the production of construction works;
2) the costs associated with the maintenance of the production process;
3) non-capital costs associated with the process of improving building technologies, increasing productivity and quality in certain types of work, etc.
We can distinguish: a) current costs - for the operation of treatment facilities, environmental protection measures, etc.; b) additional costs (for example, for the production of work on a rotational basis); c) other expenses.
The components of the financial result (profit or loss) of the activities of the construction organization:
–?financial result from the delivery to the customer of objects, works and services provided for by the contracts;
-? the financial result from the sale to the side of fixed assets, other property of the organization, products and services of auxiliary and auxiliary industries that are on the balance sheet of the construction organization, as well as income from non-sales operations, reduced by the amount of expenses on them.
Profit (loss) from the delivery of construction objects to the customer, as well as from the performance of other works stipulated by the contract, is calculated as the difference between the proceeds from their sale at the prices established in the contract, without value added tax and other deductions provided for by law, and the costs of their production and distribution.
Knowledge and consideration of all the features of the functioning of finance in the field of capital construction, as well as an understanding of the features of each stage of the organization of construction work, methods of their production are necessary to achieve the maximum financial result in this area of production.
This text is an introductory piece. author Chernyshev V. E.2.1. The place of accounting in the management system of a construction organization Improving the quality of the management system of a construction organization is inextricably linked with the improvement of accounting, which makes it possible to monitor and analyze the achievement of certain goals,
From the book Organization of management accounting in construction author Chernyshev V. E.Chapter 5 Pricing policy of the construction organization 5.1. Essence and goals of pricing policy The main goal of management accounting in a construction organization is to provide management at different levels with information to make timely and informed decisions.
From the book Organization of management accounting in construction author Chernyshev V. E.5.3. Directions of the pricing policy of the construction organization The pricing policy and strategy must comply with a specific marketing strategy of the construction organization. At the same time, the goals of such a strategy may be: penetration into a new market
From the book Organization of management accounting in construction author Chernyshev V. E.Chapter 6 Fundamentals of the financial policy of the construction organization 6.1. Goals and objectives of financial policy The purpose of developing a financial policy for a construction organization is to build an effective financial management system aimed at achieving strategic
From the book Organization of management accounting in construction author Chernyshev V. E.6.3. Financial management system of a construction organization As the experience of countries with developed economies shows, an effective financial management system based on the development of a financial business plan is necessary for the successful functioning of an organization. AT
From the book Organization of management accounting in construction author Chernyshev V. E.9.3. Automation of management accounting of a construction organization
From the book Accounting and Taxation in Construction author Sosnauskene Olga Ivanovna1. Implementation of investment and construction activities Investment activities are investments, and the implementation of practical actions in order to make a profit or achieve another beneficial effect. In accordance with Art. 1 Federal Law dated
From the book Accounting author Bychkova Svetlana MikhailovnaThe impact of shortages and losses from damage to valuables on the financial result The formation of the financial result is directly affected by shortages and losses of material assets, as they are withdrawn from circulation. In terms of accounting for financial results
From the book Accounting in trade author Sosnauskene Olga Ivanovna7.1. Financial result: basic concepts The final result of the activities of a trade organization for a certain period is called the financial result or profit (loss). The financial result reflects all aspects of the activities of a trade organization: 1) profit (or
From the book Accounting: Cheat Sheet author Team of authors63. Financial result from the activities of the organization This result is the balance of income and expenses received by it. According to PBU 9/99 and 10/99, the organization receives income and incurs expenses for ordinary activities, as well as other expenses. Income from ordinary types
From the book 1C: Managing a small firm 8.2 from scratch. 100 lessons for beginners author Gladkiy Alexey AnatolievichLESSON 98 Note that before generating this report
author Chipurenko Elena Viktorovna4.2. Assessment of the impact of VAT on the financial result Reflecting the accrual of tax by posting D-t 91 K-t 68 (for example, tax on property of organizations) is understood as the payment of tax at the expense of the financial result. This means that the amount of tax is treated as an expense that affects
From the book The tax burden of an enterprise: analysis, calculation, management author Chipurenko Elena Viktorovna4.3. Special cases of occurrence of VAT liabilities and their impact on the financial result
From the book The tax burden of an enterprise: analysis, calculation, management author Chipurenko Elena Viktorovna4.8. Calculation of the impact of taxes included in the cost on the financial result
From the book The founder and his company [From the creation of an LLC to exit from it] author5.2. Financial result as the basis for paying dividends In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 28 of Law No. 14-FZ, dividends are paid out of the company's net profit. Therefore, the basis for declaring dividends is the presence of net profit, the value of which is reflected
From the book Founder and his company: all questions [From creation to liquidation] author Anishchenko Alexander Vladimirovich4.2. Financial result as the basis for paying dividends In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 28 of Law No. 14-FZ, dividends are paid out of the company's net profit. Therefore, the basis for declaring dividends is the presence of net profit, the value of which
The general procedure for recognizing income for accounting is determined by PBU 9/99. The proceeds from the performance of work on the construction of the facility is for the contracting construction organization income from ordinary activities and is taken into account in the amount of the total estimated cost (price) of the facility (clauses 5, 6 PBU 9/99).
Based on clause 16 of PBU 2/94, the contractor can apply two methods for calculating the financial result, depending on the accepted forms for determining income:
on the value of the object as a whole;
at the cost of individual work performed.
Using the method of determining the proceeds from the sale by the cost of the object as a whole provides for determining the financial result of the contractor upon the complete completion of work under the construction contract as the difference between the contractual value of the completed construction of the object and the costs of its production. At the same time, all accumulated costs for the production of construction and installation works until their full completion is work in progress. Write-off of costs, reflection of sales proceeds and determination of the financial result of the contractor are carried out only after the complete completion of work at the construction site and the signing of an act in the form N KS-11 or an act in the form N KS-14. Up to this point, all funds received by the contractor for the performance of work are accounted for as advances received (clause 5 of PBU 2/94). Receipts in the form of advance payments for goods, works, services in accordance with paragraph 3 of PBU 9/99 are not recognized as income of the organization.
In the accounting of the contractor, the amounts of advances received from the customer are reflected in the entry:
Debit 51, Credit 62 - an advance payment was received for the performance of work under a work contract,
Debit 62, Credit 68 - VAT was charged on the amount of advances received.
The contractor has the right to deduct the amount of VAT calculated and paid to the budget from the advance payment received, after the turnover on the implementation of construction and installation works is reflected in the accounting records and VAT is charged on the turnover on the implementation (clause 8 of article 171, clause 6 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ):
Debit 62, Credit 90-1 - reflected the proceeds from the implementation of construction and installation works,
Debit 90-3, Credit 68 - VAT charged on revenue,
Debit 90-2, Credit 20 - the actual cost of completed construction and installation work was written off,
Debit 90-9, Credit 99 - reflects the profit from the implementation of construction and installation works,
Debit 68, Credit 62 - accepted for VAT deductions, calculated and paid from the amounts of advances.
Since the production cycle of construction work on one object is quite long, the use of the method of determining the proceeds from the sale at the cost of the object as a whole is possible only when building small objects or when performing certain types of construction and installation works at the object.
When applying the method of determining income as individual works on structural elements or stages are completed, the financial result of the contractor is revealed for a certain reporting period after the complete completion of individual works on structural elements or stages provided for by the project, as the difference between the amount of work performed and the costs attributable to them ( clause 17 PBU 2/94). In this case, structural elements or stages must be identified in the approved design and estimate documentation for construction. The volume of work performed is determined in accordance with the established procedure based on their contractual value, including the amount of VAT charged. The costs attributable to the work performed are allocated by the direct method and (or) by calculation.
The use of this method of calculating the financial result is allowed if the volume of work performed and the costs attributable to them can be sufficiently estimated.
To summarize information about the stages of work completed in accordance with the concluded contracts that have independent significance, account 46 "Completed stages of work in progress" is used.
When applying the method of determining sales proceeds at the cost of individual work performed, the following accounting entries are made:
Debit 46, Credit 90-1 - reflected the proceeds from the implementation of the completed stage of construction and installation work (an act of acceptance of work performed is drawn up - form N KS-2),
Debit 90-3, Credit 68 - reflected VAT on revenue (for organizations calculating VAT in accordance with the accounting policy at the time of shipment),
Debit 90-2, Credit 20 - the actual cost of the completed construction and installation stage was written off.
At the end of the month, the financial result (profit or loss) from the implementation of the completed construction and installation stage is determined:
Debit 90-9, Credit 99 - reflects the profit from the implementation of the completed stage of construction and installation work.
The amounts of funds received from customers in payment for completed and accepted stages are reflected in the entry:
Debit 51, Credit 62 - reflects the amount of advances received.
Account 46 is closed only after completion of all stages of work. Thus, in fact, after signing the act in form N KS-11 or the act in form N KS-14, an entry is made in accounting:
Debit 62, Credit 46 - the contractual cost of the stages was written off upon completion of the work as a whole.
Based on clause 19 of PBU 2/94, the choice of one of the described methods for determining the financial result is made by the contractor, depending on the degree of reliability of estimating the cost of the work performed and the costs attributable to them on the construction site. At the same time, the contractor may use two of the above methods when determining the financial result from the implementation of contract work when accounting for work performed under various construction contracts.
In addition, a construction contractor may apply another method of income recognition based on PBU 9/99. According to paragraph 13 of this Regulation in accounting, an organization may recognize revenue from the performance of work with a long cycle of performance as the work is ready or upon completion of the work as a whole. This means that in the accounting of the contractor, calculations are allowed not only after the completion of all work under the agreement (contract) or for finished structural elements and stages, but also according to the percentage of readiness of these elements agreed by the parties to the contract. Revenue from the performance of a specific job is recognized in accounting as soon as it is ready, only if the readiness of the work can be determined.
In relation to works that are different in nature and conditions of performance, an organization can simultaneously apply in one reporting period different methods of revenue recognition provided for by PBU 9/99. In our opinion, when using this method, the construction contracting organization, when accounting for sales proceeds until the completion of all work under the contract, can also use account 46 by opening a separate sub-account for it. Information on the method for determining the readiness of work, the proceeds from which are recognized as soon as they are ready, is subject to disclosure in the financial statements and is an element of the organization's accounting policy (clause 17 PBU 9/99).